A women's health journey can certainly be complex and taking care of your health should be a priority. It should however also be an enjoyable one. Through expert guidance and compassionate care, we strive to find that perfect balance to make your journey as easy and stress-free as possible. .
Endometriosis is a painful disorder in which the tissue that normally lines the inside of your uterus, grows on the outside of the uterus. Endometriosis involves your ovaries, bowel or the tissue lining your pelvis. Rarely, endometrial tissue may spread beyond your pelvic region. In endometriosis, displaced endometrial tissue continues to act as it normally would — it thickens, breaks down and bleeds with each menstrual cycle. Because this displaced tissue has no way to exit your body, it becomes trapped. When endometriosis involves the ovaries, cysts may form. Surrounding tissue can become irritated, eventually developing scar tissue and adhesions — abnormal tissue that binds organs together.
Pelvic pain is common during pregnancy. This is because ligaments are stretching, hormone levels are changing, and organs are shifting around to make room for your growing uterus. However, sometimes pain is a red flag that something more serious is wrong. Your pelvis is mainly formed of two pubic bones that curve round to make a cradle shape. The pubic bones meet at the front of your pelvis, at a firm joint called the symphysis pubis.
The joint's connection is made strong by a dense network of tough tissues (ligaments). During pregnancy, swelling and pain can make the symphysis pubis joint less stable, causing pelvic pain.

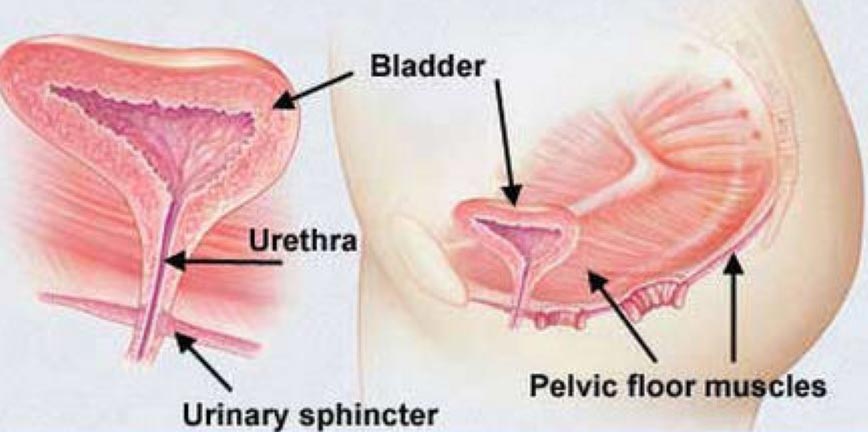
There are different kinds of surgeries used to correct stress incontinence, which occurs when weakened pelvic floor muscles allow the bladder neck and urethra to drop. These surgeries seek to lift the urethra or the bladder - or both - into the normal position. This makes sneezing, coughing, and laughing less likely to make urine leak from the bladder.
Surgery works to cure stress incontinence better than any other treatment. If other treatments - like pelvic floor muscle exercises - haven't worked to control your incontinence, surgery may be your best option. The surgery you will undergo depends on your preference and your health.
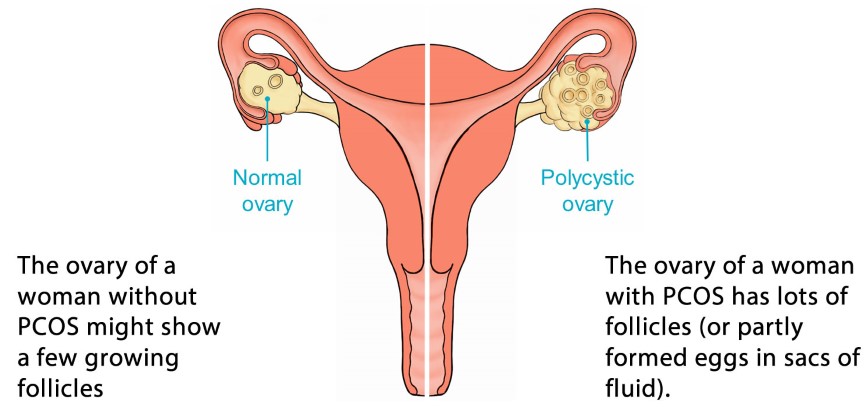
Polycystic ovary syndrome (PCOS) is defined as chronic anovulation with evidence of hyperandrogenism, after the exclusion of secondary causes. It is commonly linked to obesity and the presence of the metabolic syndrome. Polycystic ovaries are very common and can affect up to 20% of women. However, the majority of women with polycystic ovaries do not have features of polycystic ovary syndrome (PCOS) and do not require intervention. Prevalence figures vary depending on diagnostic criteria used, but PCOS is thought to affect 5-15% of women of reproductive age.
The cause remains unclear. Polycystic ovaries develop when ovaries are stimulated to produce excessive amounts of male hormones, particularly testosterone. This stimulation is caused by excess LH produced by the anterior pituitary in response to increased gonadotrophin-releasing hormone (GnRH) pulsatility, or through high levels of insulin caused by insulin resistance.
We offer confidential sexual health screening (STI/STD tests) 6 days a week. We use the latest technology to make screening even easier than before, with touchscreen check-in, self-taken tests and fast bloods with our friendly team. If you're at risk it's important to get tested.
If you are worried about a specific sexual encounter, you may want to delay your visit. There's a time gap between catching an infection and it appearing on the tests. Testing earlier might miss something. This is called the window period. We'd recommend waiting 4 weeks to put your mind at rest. You may need urgent treatment if you have had a significant HIV risk in the last 72 hours (eg unprotected anal sex).
Fertility treatments are most likely to benefit women whose infertility is due to problems with ovulation. Treatment is least likely to benefit infertility caused by damage to the fallopian tubes or severe endometriosis.
The first step of treating infertility in many cases is to treat the underlying cause of infertility. For example, in cases where thyroid disease causes hormone imbalances, medication for thyroid disease may be able to restore fertility. The most common medications used to treat infertility help to stimulate ovulation.
Hormone Replacement Therapy (also known as hormone therapy, menopausal hormone therapy, and oestrogen replacement therapy) uses female hormones -- oestrogen and progesterone -- to treat common symptoms of menopause and aging. Doctors can prescribe it during or after menopause.
After your period stops, your hormone levels fall, causing uncomfortable symptoms like hot flashes and vaginal dryness, and sometimes conditions like osteoporosis. HRT replaces hormones your body no longer makes. It’s the most effective treatment for menopause symptoms.
Menopause is defined as the state of an absence of menstrual periods for 12 months. The menopausal transition starts with varying menstrual cycle length and ends with the final menstrual period. Perimenopause is a term sometimes used and means "the time around menopause." It is often used to refer to the menopausal transitional period. It is not officially a medical term, but is sometimes used to explain certain aspects of the menopause transition in lay terms. "Postmenopausal" is a term used to as an adjective to refer to the time after menopause has occurred. For example, doctors may speak of a condition that occurs in "postmenopausal women." This refers to women who have already reached menopause.

Pre-menstrual tension (also known as a Pre-menstrual syndrome and PMS) is the physical and emotional symptoms that occur within the week before a woman starts her period. Symptoms usually vary between women and resolve around the first day of the period. Common symptoms of pre-menstrual tension include acne, tender breasts, bloating, fatigue, irritability and mood changes. These symptoms are often present for up to six days.
Diagnosis requires a consistent pattern of emotional and physical symptoms occurring after ovulation and before menstruation to a degree that interferes with normal life. Emotional symptoms must not be present during the initial part of the menstrual cycle. A daily list of symptoms over a few months may help in diagnosis. Other disorders that cause similar symptoms need to be excluded before a diagnosis is made.

Menopause is defined as the state of an absence of menstrual periods for 12 months. The menopausal transition starts with varying menstrual cycle length and ends with the final menstrual period. Perimenopause is a term sometimes used and means "the time around menopause." It is often used to refer to the menopausal transitional period. It is not officially a medical term, but is sometimes used to explain certain aspects of the menopause transition in lay terms. "Postmenopausal" is a term used to as an adjective to refer to the time after menopause has occurred. For example, doctors may speak of a condition that occurs in "postmenopausal women." This refers to women who have already reached menopause.
Labia reconstruction (also known as labiaplasty, labia minora reduction and labia reduction) is a term used to describe the procedure of altering the labia minora (the inner labia) and the labia majora (outer labia) – the folds of skin that surround the human vulva. There are two main categories of women seeking cosmetic genital surgery: those with congenital conditions such as intersex, and those with no underlying condition who experience physical discomfort or wish to alter the appearance of their genitals because they believe they do not fall within a normal range
The size, colour, and shape of labia vary significantly, and may change as a result of childbirth, aging and other events. Labia reconstruction addresses congenital defects and abnormalities such as vaginal atresia (absent vaginal passage), Müllerian agenesis (malformed uterus and fallopian tubes), intersex conditions (male and female sexual characteristics in a person); and tearing and stretching of the labia minora caused by childbirth, accident and age.